Seed certification
 Why are seeds certified?
Why are seeds certified?
The purpose of seed certification is to maintain and make available to farmers high-quality and genetically pure seeds of superior cultivars. Certified seed is high in genetic purity, high in germination and vigor, and of good quality (i.e., free from disease and from damaged or immature seed).
Classes of seeds
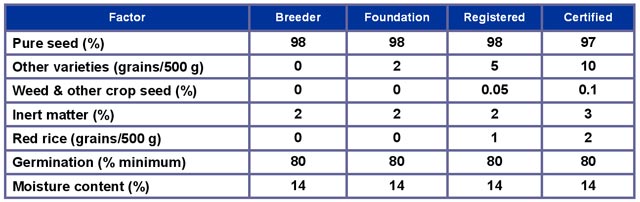
Breeder seed - this is the seed of a new variety that has the highest purity and is produced, developed, controlled, and provided directly by breeders or their institutions for further multiplication.
Foundation seed - this is the progeny of the breeder seed, produced by trained officers of an agricultural station in conformity with regulated national standards and handled to maintain genetic purity and identity of the variety.
Registered seed - this is the progeny of the foundation seed grown by selected farmers, handled to maintain genetic purity and identity, and has undergone field and seed inspections to ensure conformity with standards.
Certified seed - this is the progeny of foundation, registered, or certified seeds, handled to maintain sufficient varietal identity and purity, grown by selected farmers under prescribed conditions of culture and isolation, and subjected to field and seed inspections prior to approval by the certifying agency. Harvest from this class is used for commercial planting.
Seed testing
Seed samples are collected and submitted for laboratory analysis after drying and processing. Tests conducted include those that determine
- Varietal purity
- Weed and other crop seed
- Inert material
- Other varieties
- Red rice
- Germination
- Moisture content
Different countries set standards for the various factors considered in seed certification.
Official standards for seed certification in Philippines
For more information:
Visit the Rice Knowledge Bank website (http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org), email postharvest@irri.org; or call +63 2 580 5600.