|
|
|
Post production: Drying |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Machine drying |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Describe the different types of dryers and their proper use. |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Mechanically dried grain will produce better quality rice than sun dried grain
|
|
What is a mechanical dryer?
A mechanical way to remove the water from wet grains by blowing (heated) air through the grain. This drying is done until the grain has the desired moisture content.
Most dryers have the following components:
What is the difference of mechanical drying with sun drying?
Mechanical drying has some advantages over sun drying:
Since rice quality is becoming more important to rice consumers, medium-sized grain dryers have become a common sight throughout Asia. For production of premium quality rice or seed, mechanical drying with heated air dryers is highly recommended. |
|
||||
|
|
|
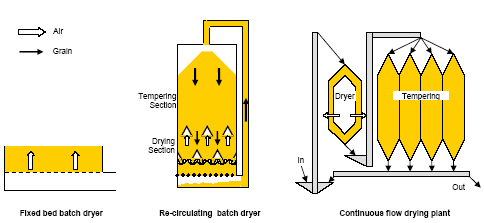
The different types of dryers
The most common way of characterizing heated air drying systems is through the description of the way how the grain is being held in or flows through the system. Here we differentiate between fixed bed batch dryers, re-circulation batch dryers and continuous flow dryers:
The most common types of grain dryers in Asia are the fixed bed dryer and the re-circulating batch dryer. They are both batch-fed dryers meaning that a certain quantity of grain is loaded and dried before the dryer is unloaded and a new batch can be dried.
|
|
||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Don't forget!
Important: Monitor the drying process!
|
|
|||||
Next lesson |
|
This ends our module on drying. Next, we discuss storage. |
|
||||

![obj[1]](obj_1_.gif)